Receptor Mediated Endocytosis: Unlocking Cellular Secrets
Receptor mediated endocytosis (RME) is a fascinating cellular process that allows cells to selectively uptake specific molecules from their surroundings. This mechanism plays a crucial role in various biological functions, including nutrient absorption, signal transduction, and even the entry of certain viruses into cells. By understanding RME, scientists can unlock secrets to developing targeted therapies, improving drug delivery systems, and advancing our knowledge of cellular behavior. Whether you're a researcher, student, or simply curious about cellular processes, this blog will delve into the intricacies of RME, its significance, and its applications, receptor mediated endocytosis, cellular processes, drug delivery systems.
What is Receptor Mediated Endocytosis?
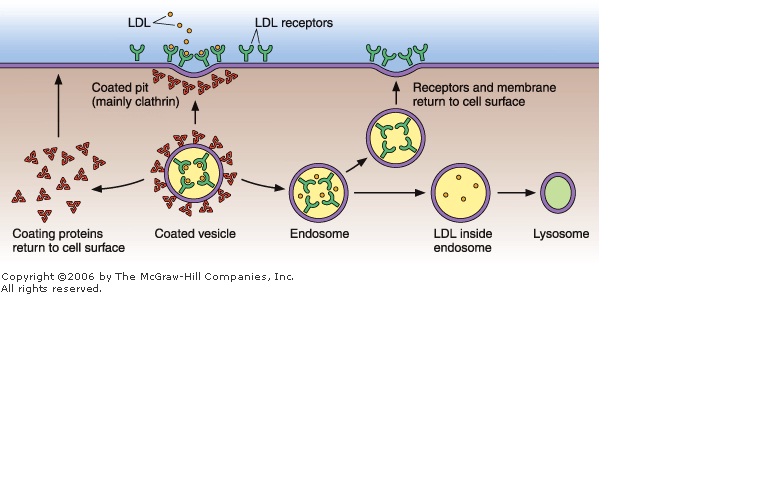
Receptor mediated endocytosis is a highly regulated process where cells internalize extracellular molecules by binding them to specific receptors on the cell membrane. Unlike other forms of endocytosis, RME is selective, ensuring that only particular substances are transported into the cell. This process is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to external stimuli, receptor mediated endocytosis, cellular homeostasis, endocytosis types.
The Mechanism of Receptor Mediated Endocytosis

Step 1: Binding of Ligand to Receptor
The process begins when a ligand—such as a protein, hormone, or virus—binds to its specific receptor on the cell surface. This binding triggers a conformational change in the receptor, signaling the cell to initiate endocytosis, ligand binding, cell surface receptors.
Step 2: Formation of Coated Pits
Once the ligand-receptor complex forms, the cell membrane invaginates, creating a coated pit. This pit is lined with clathrin, a protein that provides structural support and facilitates the formation of vesicles, clathrin coated pits, membrane invagination.
Step 3: Vesicle Formation and Internalization
The coated pit deepens and eventually pinches off from the cell membrane, forming a vesicle containing the ligand-receptor complex. This vesicle, known as an endosome, is then transported into the cytoplasm for further processing, vesicle formation, endosome function.
Step 4: Sorting and Trafficking
Inside the cell, the endosome undergoes sorting. The ligand may be released for degradation or recycled back to the cell membrane, while the receptor is often returned to the surface for reuse. This step ensures efficient resource utilization, intracellular sorting, receptor recycling.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Receptor | Binds specific ligands on the cell surface |
| Clathrin | Forms coated pits for vesicle creation |
| Endosome | Transports internalized material within the cell |

Applications of Receptor Mediated Endocytosis

Drug Delivery Systems
RME is leveraged in designing targeted drug delivery systems. By attaching drugs to ligands that bind specific receptors, therapies can be delivered directly to affected cells, minimizing side effects and improving efficacy, targeted therapy, drug delivery innovations.
Research and Diagnostics
Understanding RME helps researchers study cellular uptake mechanisms and develop diagnostic tools. For instance, fluorescently labeled ligands can track receptor activity in real-time, advancing our understanding of diseases like cancer and diabetes, cellular research, diagnostic tools.
💡 Note: Receptor mediated endocytosis is distinct from other endocytic pathways due to its specificity and dependence on receptor-ligand interactions.
Summary and Checklist
Receptor mediated endocytosis is a vital cellular process with wide-ranging applications. Below is a checklist to recap key points:
- Understand the role of ligand-receptor binding in initiating RME.
- Recognize the importance of clathrin in vesicle formation.
- Explore applications in drug delivery and research.
In summary, receptor mediated endocytosis is a sophisticated mechanism that highlights the precision of cellular processes. Its applications in medicine and research underscore its importance in advancing scientific knowledge and improving healthcare. By studying RME, we unlock new possibilities for treating diseases and enhancing our understanding of life at the cellular level, receptor mediated endocytosis, cellular research, drug delivery systems.
What is the difference between receptor mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis?
+
Receptor mediated endocytosis is selective and involves specific ligand-receptor interactions, while phagocytosis is non-selective and involves engulfing large particles like bacteria.
How is RME utilized in cancer treatment?
+
RME is used to deliver targeted drugs to cancer cells by attaching chemotherapy agents to ligands that bind receptors overexpressed on cancer cells.
Can viruses exploit receptor mediated endocytosis?
+
Yes, some viruses, like the influenza virus, use RME to enter host cells by binding to specific receptors on the cell surface.

