Mastering Histograms: A Quick Guide to Reading Data Visuals
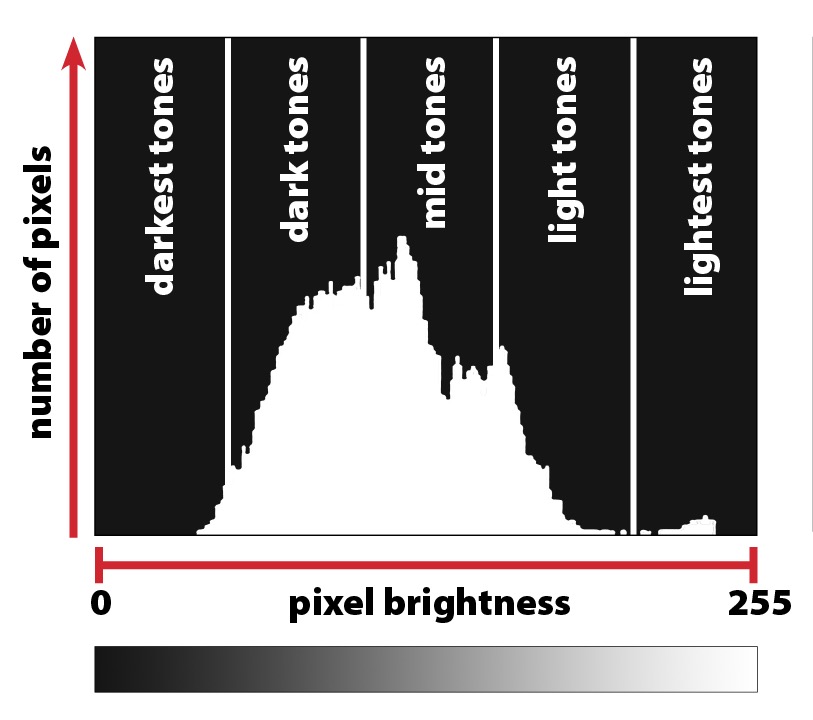

Histograms are powerful tools for visualizing data distributions, making complex information easier to understand. Whether you're analyzing sales trends, customer behavior, or scientific data, mastering histograms can help you make data-driven decisions with confidence. This guide will walk you through the essentials of reading histograms, from understanding their structure to interpreting key insights. By the end, you'll be equipped to leverage histograms effectively in your data analysis workflows, (data visualization, data analysis, histogram tutorial)
What is a Histogram?

A histogram is a graphical representation of data distribution, where data is grouped into continuous ranges called bins. Unlike bar charts, histograms show the frequency or density of data points within these bins, providing insights into patterns, skewness, and outliers. They are particularly useful for identifying trends and anomalies in large datasets, (data distribution, histogram vs bar chart, data trends)
Key Components of a Histogram
To read a histogram effectively, familiarize yourself with its core elements:
- Bins: The intervals or ranges into which data is grouped.
- Frequency: The number of data points in each bin, often represented by bar height.
- X-axis: Displays the data range or variable being measured.
- Y-axis: Represents the frequency or density of data points in each bin.
📊 Note: Properly adjusting bin size is crucial for accurate interpretation. Too few bins can oversimplify data, while too many can introduce noise, (histogram components, bin size, data interpretation)
How to Interpret Histograms

Interpreting histograms involves analyzing their shape, spread, and peaks:
Shape
The shape of a histogram reveals the distribution of data:
- Symmetric: Data is evenly distributed around the center.
- Skewed: Data is skewed to the left or right, indicating asymmetry.
- Bimodal: Two distinct peaks suggest multiple data clusters.
Spread
The width of the histogram indicates the variability of the data. Wider histograms show greater spread, while narrower ones indicate less variability, (histogram shape, data skewness, data spread)
Practical Tips for Using Histograms

To maximize the utility of histograms, consider these tips:
- Experiment with bin sizes to find the optimal representation of your data.
- Use histograms alongside other visualizations like box plots for comprehensive analysis.
- Leverage tools like Excel, Python (Matplotlib), or Tableau for creating and customizing histograms.
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| Excel | Quick, basic histograms |
| Python (Matplotlib) | Customizable, advanced analysis |
| Tableau | Interactive, professional visualizations |

🛠️ Note: Always label axes and provide context to ensure clarity for your audience, (histogram tools, data visualization tools, histogram best practices)
Histogram Mastery Checklist

- Understand the difference between histograms and bar charts.
- Identify key components: bins, frequency, X-axis, Y-axis.
- Analyze shape (symmetric, skewed, bimodal) and spread.
- Experiment with bin sizes for optimal representation.
- Use tools like Excel, Python, or Tableau for creation and customization.
Mastering histograms is an essential skill for anyone working with data. By understanding their structure, interpreting their shapes, and applying practical tips, you can unlock valuable insights from your datasets. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced analyst, histograms offer a clear and concise way to visualize data distributions. Start applying these techniques today and elevate your data analysis game, (histogram mastery, data insights, data visualization techniques)
What is the difference between a histogram and a bar chart?
+
A histogram groups data into continuous ranges (bins) to show distribution, while a bar chart compares discrete categories using bars of varying heights, (histogram vs bar chart, data visualization)
How do I choose the right bin size for a histogram?
+
Start with a default bin size and adjust based on data clarity. Too few bins oversimplify, while too many introduce noise. Tools like the Freedman-Diaconis rule can help, (bin size, histogram best practices)
Can histograms show outliers in data?
+
Yes, histograms can reveal outliers as bars with significantly lower frequencies or as gaps in the data distribution, (data outliers, histogram analysis)


